Managing Processes from the Command
Line
Instead of using the Activity Monitor, you can
determine the currently running processes from the command line
using the ps or top commands.
Use top to view a regularly updated
view of system utilization, including memory usage, page faults,
and the set of currently executing processes.
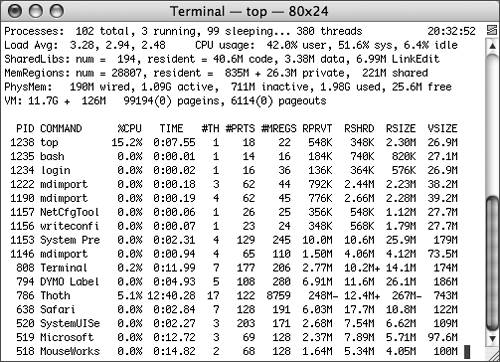
In the leftmost
column of top's tabular output, you will find the process
identifier (PID) associated with that process. You can also use the
ps command to determine the PID of a process. The PID is
used to send a message to a particular process. For example, the
command
ps -auxww | grep
TextEdit
prints the PID and other information for the
TextEdit process.
You can send signals from the CLI to running
processes requesting actions such as rereading a configuration
file, logging additional information, or quitting. For example,
with the kill command, you can send a signal to a process
with a specified PID. The command
kill -TERM
PID
asks the process with the given PID to
terminate.
To force quit a process from the command line,
use the kill signal as follows:
kill -KILL
PID
The killall command allows you to
signal processes using the name of the process rather than the PID.
The command
killall -KILL
TextEdit
force quits all processes that belong to you
with the name TextEdit.

|