Protecting Your Mac with the Mac OS X
Firewall
Because other people can access your computer
when it's on a network, you should protect it from unauthorized
traffic. Mac OS X includes firewall software you can use to block
unwanted network connections and prevent unauthorized network
access to your computer. The firewall uses the BSD utility ipfw (IP
Firewall) to block network traffic on specific IP ports.
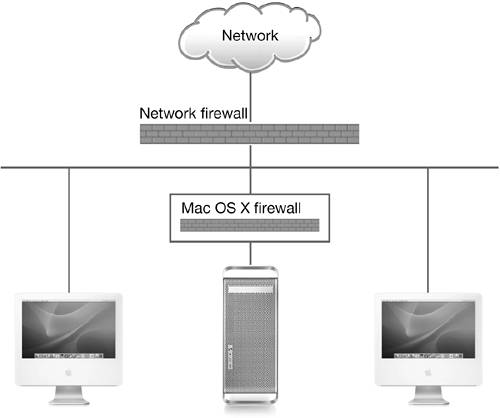
The firewall included in Mac OS X is separate
from network firewalls or network security devices that network
administrators use to protect against attacks from outside the
network, but it has the same function: it protects your computer
from attacks or unwanted intrusion. If your computer is on a
network that has a firewall, you should still use the Mac OS X
firewall to protect against the possibility of attacks from other
computers on the network.
TIP
All Mac OS X computers connected to the
Internet, including those behind network firewalls, should enable
the firewall.
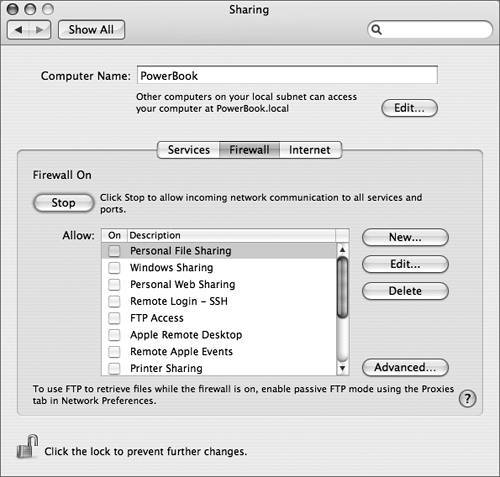
To enable the firewall, click Firewall in
Sharing preferences and then click the Start button. The Mac OS X
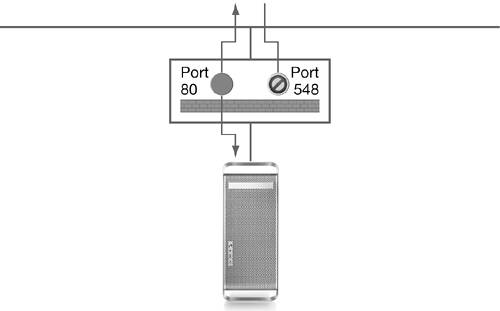
firewall blocks traffic to specific IP ports. IP ports specify
network services, such as Apple File Service (port 548) and web
services (port 80). By preventing incoming traffic from reaching
certain port numbers, you can prevent many types of unauthorized
access to your computer.
When you enable the
firewall, all ports other than the ones checked in the list will be
blocked. Blocking ports may disrupt services such as iChat Bonjour
browsing and iTunes music sharing, so be sure to block only those
ports you know are not in use.
When you turn on a network service in the
Services pane of Sharing preferences, Mac OS X automatically allows
that service in the Firewall pane. This allows authorized traffic
to pass and other traffic to continue to be blocked.
If you are curious about the ports typically
used for certain services, open /etc/services file. To read the
file contents, either use the command line or navigate to /etc
using Go to Folder (Command-Shift-G) in the Finder, and use
TextEdit to view the file contents.
You cannot change the
settings for the default ports listed in the Firewall pane;
however, you can specify additional ports to be opened as
follows:
|
1.
|
Click New.
A configuration sheet appears.
|
|
2.
|
From the Port Name pop-up menu, choose one of
the defaults and click OK, or choose Other.
Defaults have port numbers already assigned. If you choose Other,
you must specify the port number to use.
|
|
3.
|
Enter a port number, range, or series to
open.
|
|
4.
|
Enter a description of the port.
|
|
5.
|
Click OK.
|
NOTE
If you are using iTunes for Windows, refer to
Knowledge Base document 93396: "iTunes for Windows: Music Sharing
With Windows Internet Connection Firewall."
Advanced Firewall Settings
To set additional firewall options, click the
Advanced button in the Firewall pane of Sharing preferences. There
are three advanced options:
-
Block UDP
Traffic This can be helpful in preventing hackers from using
your computer as part of a denial of service attack.
-
Enable Firewall
Logging Keeps a log that shows which traffic the firewall
has allowed or denied.
-
Enable Stealth
Mode Prevents a sender from receiving any information about
denied traffic. If someone is trying to get into your computer,
they won't even know that you're preventing them from doing so
(which makes it harder for them to know if an attack is
working).
|